

Allele frequency of rare or novel variants and predicted function in 235 subjects mirrored findings from large genomic datasets. We showed accurate detection of 39 clinically relevant gene variants compared to standard genotyping techniques (99.9% concordance), including CYP2D6 CNV and UGT1A1*28. ResultsĪdequate performance of the PGxSeq panel was demonstrated with a depth-of-coverage (DOC) ≥ 20× for at least 94% of the target sequence. Identified SNVs were assessed in terms of population allele frequency and predicted functional effects through in silico algorithms. CYP2D6 CNV was determined using the bioinformatics tool CNV caller (VarSeq). NGS was carried out in 235 subjects, and sequencing performance and accuracy of variant discovery validated in clinically relevant pharmacogenes. MethodsĪ panel of capture probes was generated to assess 422 kb of total coding region in 100 pharmacogenes.
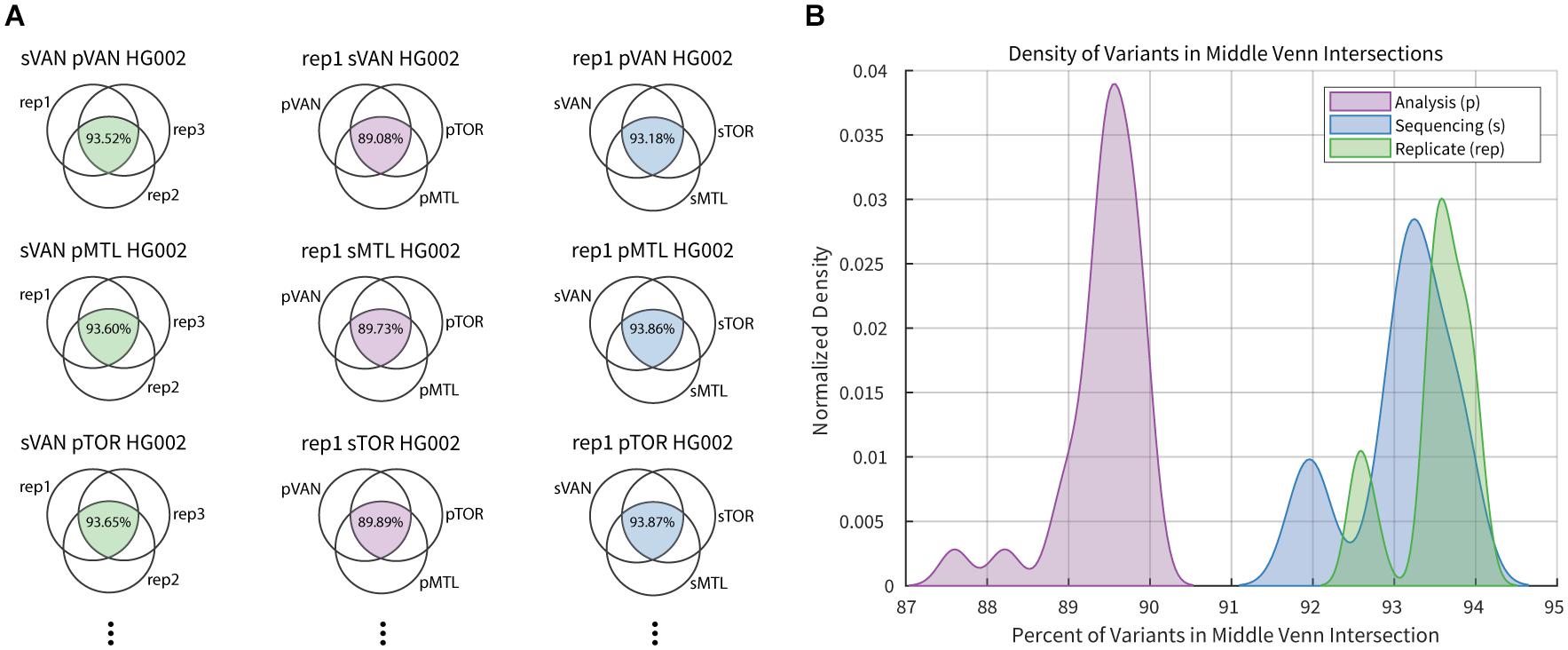
Here we developed and validated PGxSeq, a targeted exome panel for pharmacogenes pertinent to drug disposition and/or response. However, little is known regarding the utility of such panels to detect copy number variation (CNV) in the highly polymorphic cytochrome P450 ( CYP) 2D6 gene, or to identify the promoter (TA) 7 TAA repeat polymorphism UDP glucuronosyltransferase ( UGT) 1A1*28. Successful application of short-read based NGS to pharmacogenes with high sequence homology, nearby pseudogenes and complex structure has been previously shown despite anticipated technical challenges. The detection of variants contributing to therapeutic drug response or adverse effects is essential for implementation of individualized pharmacotherapy. Targeted next-generation sequencing (NGS) enables rapid identification of common and rare genetic variation.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
